Linear equations in two variables
Key Concepts: Ordered pairs/The Rectangular
Coordinate system
Solutions to equations with 2 variables
Linear equations in two variables
Intercepts
Horizontal and Vertical lines
Martin-Gaye sections and practice problems
3.1: 1 – 19 odd, 23 – 51 odd, 55, 57
3.2: 1 – 43 odd, 47, 53, 55
3.3: 1 – 10 all, 11 – 63 odd
Definitions
A solution to an equation with two variables, x and y , is an ordered pair (a,b)
where a and b are
real numbers with the property that if x = a and y = b the equation is true. The
number a is called
the x-coordinate of the ordered pair and the number b is called the y-coordinate
of the ordered pair.
Example 1
What are the x and y coordinates of the ordered pair (9,− 2) . Is the ordered
pair a solution to
the equation 3 x + 4 y = 10 + x ?
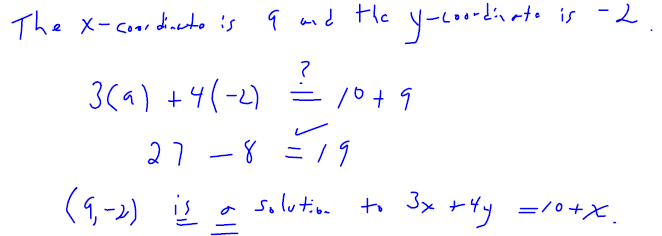
Example 2
What is the ordered pair with a x-coordinate of 5 that satisfies the equation y
= 6 x + 4
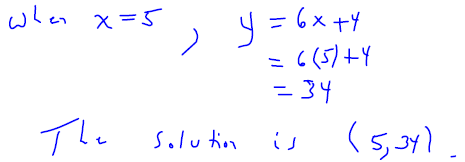
Example 3
What is the ordered pair with a y-coordinate of 5 that satisfies the equation y
= 6 x + 4
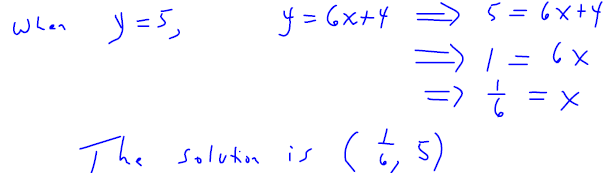
Example 4
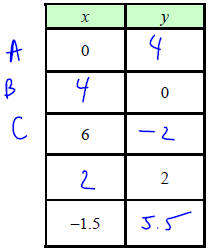
Write the missing values into Table 1 so that each implied ordered pair is a
solution to the equation
x + y = 4. Plot the four ordered pairs onto Figure 1.
| Table 1: x + y = 4
 |
 |
Example 5
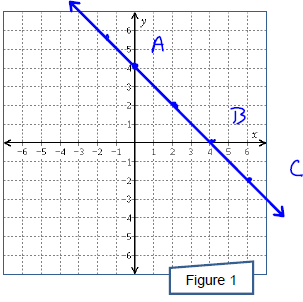
The sum of the the coordinates of each point on the line in Figure 2 is always
the same number.
What is this constant sum?
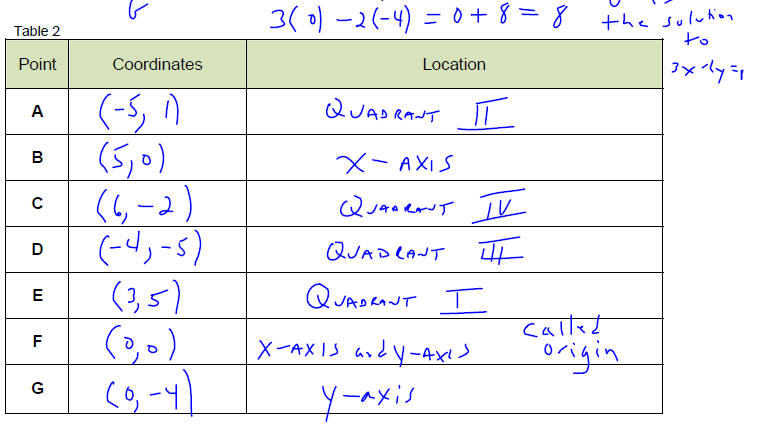
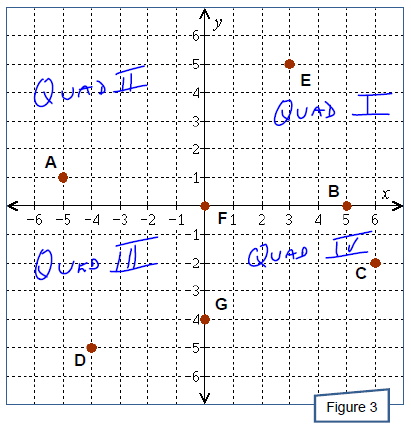
Example 6
Several points are shown in Figure 3. State the ordered pair associated with
each point and where
in the coordinate plane the point lies; assume that both coordinates of each
point are intergers.
Which point, B or F, is a solution to the equation 3x − 2 y = 8 ?
Example 7
Plot the points A(−3, 4) , B(−3, −3) , and C(5, 2) onto
Figure 4 and find the area, A, of the resultant triangle.
Assume that the scale on each axis is in centimeters.

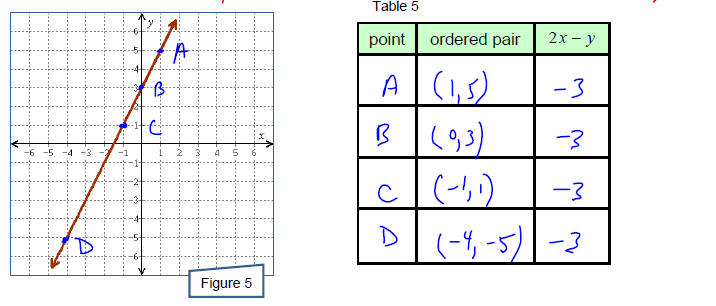
Example 8
At each point on the line in Figure 5, twice the x-coordinate minus the
y-coordinate is always the
same number. What is this common difference?
|